A Transformative Technology with Profound Legal Implications
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a technology with immense potential to change our world and every area of our daily lives. From employee use for business automation and consumer-focused generative AI tools to self-driving cars and even AI lawyering, AI is poised to be one of the most innovative technologies of our lives. The technology is so powerful that countries are vying to be leaders in AI, and industry CEOs are calling for security measures and strategic plans to foster its safe development.
Navigating the Evolving Regulatory and Ethical Landscape of AI
The significant potential of AI inevitably attracts global regulatory scrutiny, leading to the development of comprehensive legal frameworks that companies must navigate.
Global Regulatory Scrutiny and Frameworks
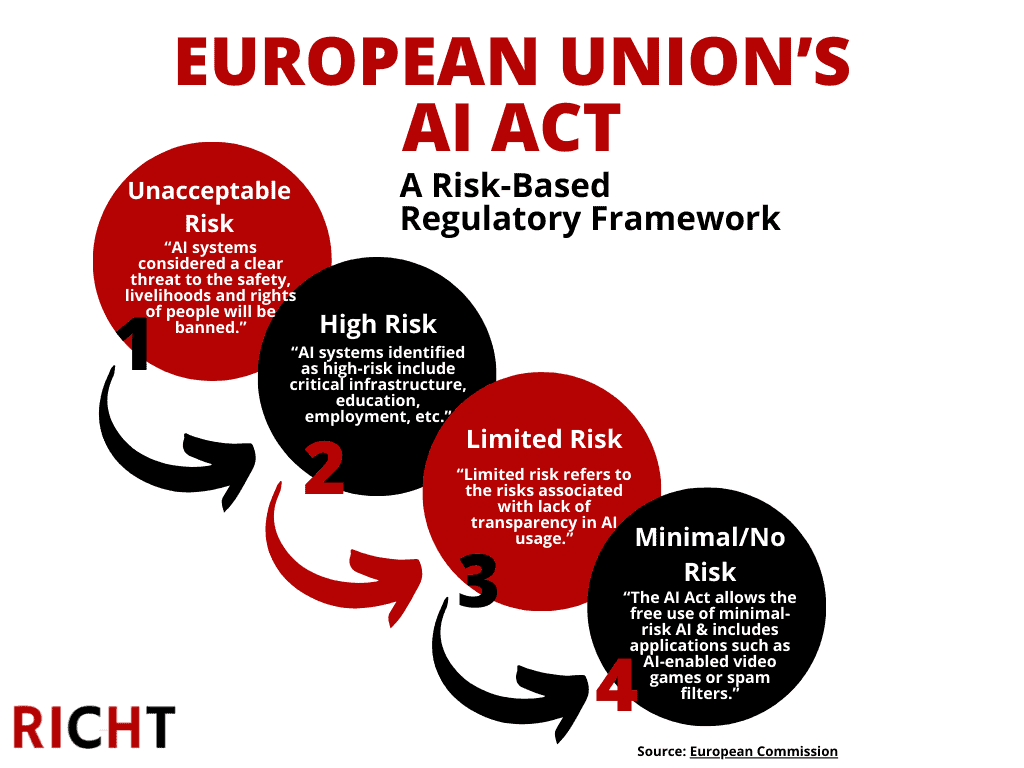
This evolving landscape encompasses the European Union’s recently enacted AI Act and emerging laws in the United States. Within the U.S., states like Utah have enacted AI legislation, Colorado has introduced its own, and a “flurry” of AI laws is emerging from California. At the federal level, the Senate has established an “AI working group,” and in July 2025, the White House released the “Winning the AI Race: America’s AI Action Plan.” International collaboration is also crucial, with countries such as the United States and the United Kingdom partnering to understand better and mitigate emerging AI risks.
Core Legal and Ethical Challenges
Beyond legislative efforts, AI presents various ethical questions and liability ramifications. There are also uncertainties about how existing intellectual property law applies to this new paradigm and how AI should be integrated into privacy law frameworks, such as the European Union’s GDPR and state laws like the CCPA.
As a nascent and rapidly evolving technology, AI’s swiftly developing capabilities bring forth novel legal questions. This is particularly true on the privacy front, with significant issues arising concerning AI and location data. Differing approaches to data processing in the AI context among various AI vendors, as well as the associated data processing agreement requirements and restrictions on AI vendors’ training on data, also demand careful consideration. Furthermore, there is heightened focus on “higher risk” or “sensitive” uses of artificial intelligence, such as potential bias in recruiting, employment monitoring, and healthcare applications.
Operational Complexities and Contractual Safeguards
Opaque terms and conditions or privacy policies that inadequately address how AI features interact with existing online terms are increasingly common pain points. This was illustrated by the public backlash Adobe received concerning its vague terms. Even for services not directly offering AI, legal considerations related to AI, such as in the M&A context, must be taken into account. These represent just a few of the myriad legal ramifications of AI, which will undoubtedly continue to evolve and expand. However, specific essential AI legal considerations should be addressed as a foundational matter.
Proactive Compliance and Regulatory Enforcement
Regulators and lawmakers are increasingly focusing on implementing legal frameworks for AI. The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) is particularly active in regulating and enforcing AI, especially concerning “deceptive or unfair conduct” under Section 5 of the FTC Act, as well as through its general AI guidance.
Furthermore, private legal actions, including class actions and other multi-district litigation (MDL), are becoming more prevalent in the artificial intelligence space, with many leading voices anticipating an imminent surge of AI-related litigation. Currently, AI tools and operations must undergo thorough AI governance and assessments to identify risks and associated compliance obligations, followed by the implementation of corresponding mitigation strategies.
Experienced AI Legal Guidance from RICHT
At RICHT, we are AI lawyers dedicated to partnering with clients to navigate the artificial intelligence landscape, stay ahead of the regulatory curve, and gain a deeper understanding of AI policy. We assist with a range of AI-related legal matters, including:
- Addressing privacy compliance and intellectual property considerations, particularly copyright law, for the development and use of large language models (LLMs).
- Drafting and negotiating vendor agreements with major LLM providers, such as Amazon’s AWS Bedrock AI offering or Microsoft’s Azure AI. This includes crucial aspects, such as limiting training on client data (a common point of contention) and ensuring adequate indemnification, among other key legal considerations.
Our goal is to empower clients to leverage AI for continued innovation while effectively managing legal risk.
Contact An AI Lawyer To Learn How We Can
Artificial Intelligence Law Services We Offer
Sectors We Serve
Technology
Financial Services
Healthcare & Life Sciences
Shipping & Logistics
MarTech
Industrials
80%
Of Enterprises Will Have Incorporated AI By 2026 (Gartner)